There are at least 11 different Heat Exchanger Types. Heat exchangers are a staple in today’s devices. They are not only present in the simplest of devices; exchangers have also found their use in big industries and machineries in the world today. They are basically devices found in some machines that enable it to transfer heat from one medium to another. They facilitate the efficient transfer of heat from one object to another.
In alphabetical order they are. Adiabatic Wheel; Fluid; Direct Contact; Dynamic Scraped Surface; HVAC Air Coils; Phase-Change; Plate; Plate Fin; Shell and Tube; Spiral; Waste Heat Recovery Units. With as many as there are they each have a very specific purpose and action to performance. So applications are very important. Hand calculations are possible but the best way to calculate is computer programs. Limitations need to be evaluated. Sometimes the cost may be considered first, but there are other criteria that will have to be processed.
Here is a brief definition of each heat exchanger:
Adiabatic Wheel — uses an intermediate fluid or solid store to hold heat.
Fluid — this has gas passing upwards through a shower of fluid for mostly water. Direct Contact — transfers the heat between hot and cold streams.
Dynamic Scraped Surface– used mainly for heating or cooling with a continuous scraping.
HVAC Air Coils — these types of heat exchangers are most often use for air conditioning vehicles and buildings.
Phase-Change — is a single phase for heating up or cooling down fluids.
Plate — multiple, thin, slightly separated plates so the fluid can flow through passages.
Plate Fin — made with aluminum alloys that provide higher heat efficiency.
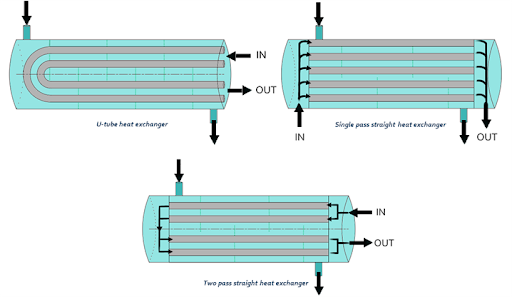
Shell and Tube — as the name suggests it is comprised of tubes. One has the fluid and the other fluid is over the tubes.
Spiral — the two channels are coil for better efficiency.
Waste Heat Recovery Units — recovers and transfers hot gas streams to water or oils.
How to choose it?
When choosing types of heat exchangers that would be best there are several things that must be taken into consideration. Tube diameter, tube length, tube pitch, tube corrugation, tube layout, and baffle design. The baffle design is use in shell and tube exchangers. This isn’t just something that can be decided strictly on price. What will it used for? What capacity will you need? Are you going to use it for gas or water or oil? What is the space size you are going to be using? There are even advantages of one heat exchanger over another one. It just depends on what is need.
We must say that double pipe heat exchangers are suitable for industrial cooling processes and Small heat transfer area requirements while sell and tube heat exchangers are used in oil refining, preheating, oil cooling processes and as steam generator, boiler in heat recovery and vapor recovery systems. Aan die ander kant, plate heat exchangers are commonly use in food and chemical processing, and furnaces.